Building a Swift package using the Swift 6 language mode

Helm Pro yearly subscribers now get a 30% discount on RocketSim thanks to contingent pricing on the App Store.
I have recently learned that some of the breaking changes that will come with Swift 6 (like full data isolation and data race safety checks) will be part of the Swift 6 language mode, which will be an opt-in feature in the Swift 6 compiler.
This means that, when you update your version of Xcode or use a Swift toolchain that uses the Swift 6 compiler, unless you explicitly enable the Swift 6 language mode, your code will be compiled using the Swift 5 language mode.
In this article, I will show you how to download and install a development snapshot of the Swift 6 toolchain and enable the Swift 6 language mode when building a Swift package.
Downloading a Swift 6 toolchain
The first step to building your code with the Swift 6 compiler and language mode is to download a Swift 6 development toolchain.
Apple makes builds of the Swift compiler from the release/6.0 branch available for numerous platforms on the swift.org website that you can download and install on your system.
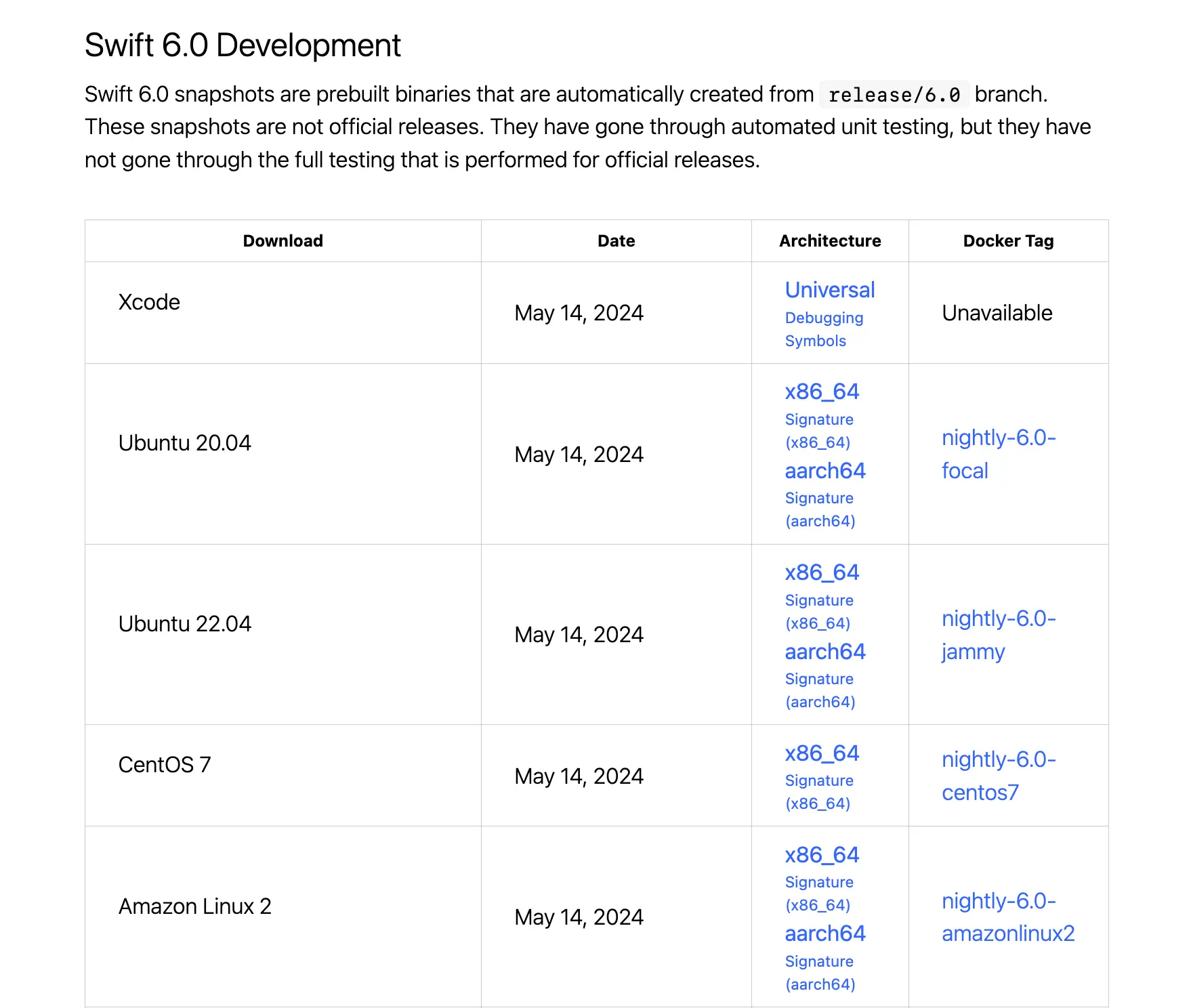
You can choose to do this manually, but I would recommend using a tool like Swiftenv for macOS or Swiftly for Linux to manage your Swift toolchains, as I am going to do in this article.
SwiftEnv - macOS
Swiftenv is a Swift version manager inspired by pyenv that allows you to easily install and manage multiple versions of Swift.
Using Swiftenv, installing the latest Swift 6 development snapshot is as easy as running the following commands:
# Install the latest Swift 6 development toolchain
swiftenv install 6.0-DEVELOPMENT-SNAPSHOT-2024-04-30-a
# CD into your Swift package directory
cd your-swift-package
# Set the Swift 6 toolchain as the default for this directory
swiftenv local 6.0-DEVELOPMENT-SNAPSHOT-2024-04-30-aSwiftly - Linux
If you’re trying to build your code on a Linux machine, you can use the Swift Server Workgroup’s Swiftly command line tool to install and manage Swift toolchains by running the following commands:
# Install the latest Swift 6 development toolchain
swiftly install 6.0-DEVELOPMENT-SNAPSHOT-2024-04-30-a
# Set the Swift 6 toolchain as the active toolchain
swiftly use 6.0-DEVELOPMENT-SNAPSHOT-2024-04-30-aTurning the language mode on in SPM
Let’s consider a Swift package target with some code that yields an error when compiled using the Swift 6 compiler and the Swift 6 language mode:
class NonIsolated {
func callee() async {}
}
actor Isolated {
let isolated = NonIsolated()
func callee() async {
await isolated.callee()
}
}Let’s build it using the Swift 6 toolchain we downloaded earlier and with the StrictConcurrency experimental feature turned on:
As you can see, the result of the build is a warning instead of an error. This is because, by default, the Swift 6 compiler uses the Swift 5 language mode and the Swift 6 language mode is opt-in.
There are two ways to enable the Swift 6 language mode: directly from the command line by passing the -swift-version flag to the swift compiler or by specifying it in the package manifest file.
Command line
To build your code with the Swift 6 language mode enabled, you can use the following command:
swift build -Xswiftc -swift-version -Xswiftc 6Package manifest
You can enable the Swift 6 language mode for your Swift Package by updating the tools-version to 6.0 and adding the swiftLanguageVersions key to the package manifest file:
// swift-tools-version: 6.0
import PackageDescription
let package = Package(
name: "Swift6Examples",
platforms: [.macOS(.v10_15), .iOS(.v13)],
products: [
.library(
name: "Swift6Examples",
targets: ["Swift6Examples"]
)
],
targets: [
.target(name: "Swift6Examples")
],
swiftLanguageVersions: [.version("6")]
)Output
Now, when you build your code with the Swift 6 language mode enabled, you will see that the error is correctly reported: